Retained earnings – the word itself sounds like big business jargon, something only men in suits talk about behind closed doors. Well, that’s not true.
Even if you are managing a small shop in your hometown or flipping burgers in your food truck, retained earnings are important. Because they reveal how much profit your business has accumulated, which you will keep with you and not distribute to shareholders.
What are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings are a portion of whatever profit you have earned and kept aside rather than distributing to shareholders. Such retention is usually done with the intention to reinvest sooner or later in your business and not for paying dividends.
In simpler terms, these accumulated profits are the ones that you will keep for your business growth instead of paying off debts.
Say, for example, you run a small business and make $12,000 profit annually after covering all fixed and variable expenses. Now, you have decided to keep the entire amount with you rather than clearing your business debts. That $12,000 is your retained earnings, which you will reinvest to buy new equipment or launch new products.
How to Calculate Retained Earnings
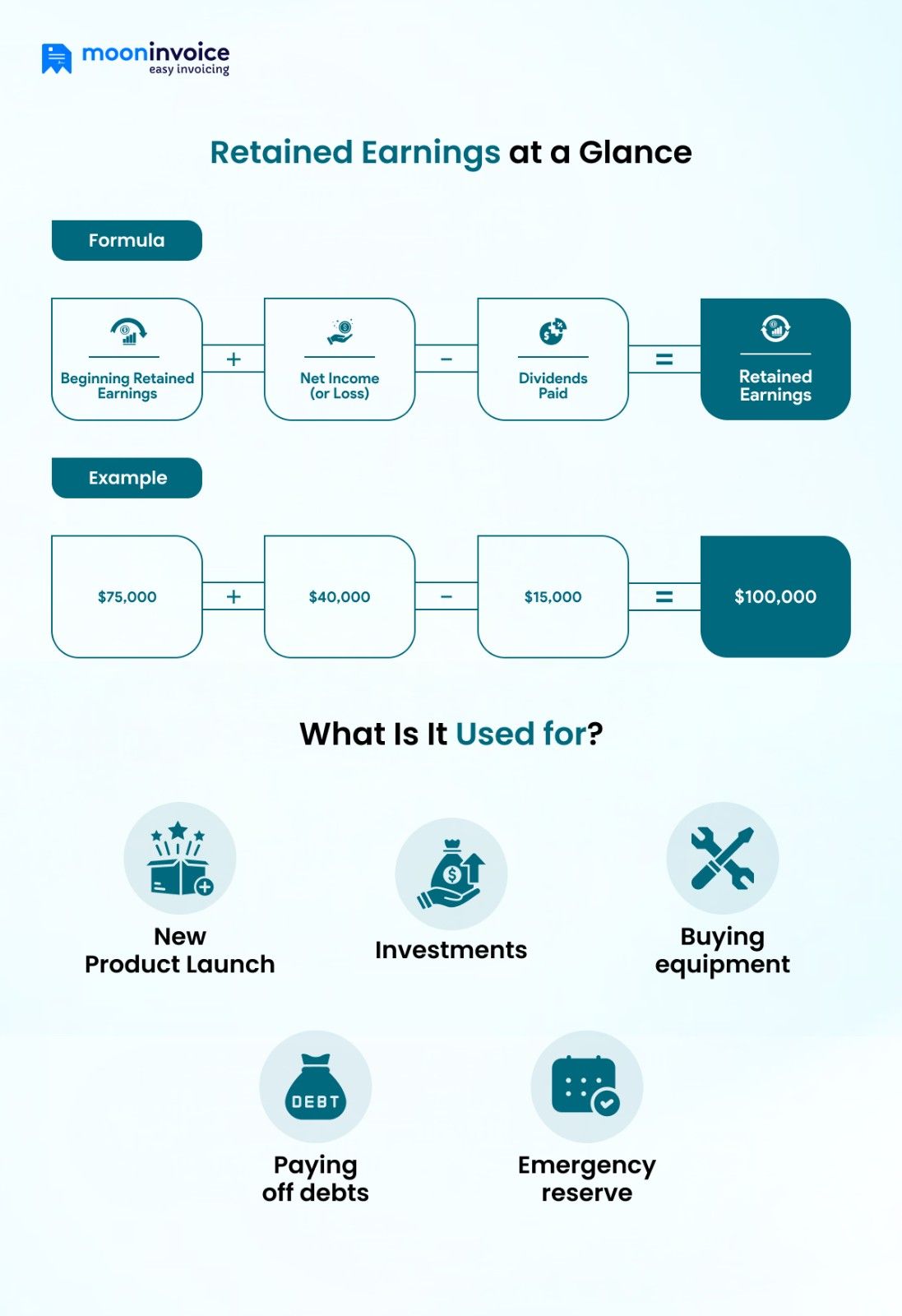
Even if you have no investors, retained earnings are still important to use your leftover money wisely and fuel your business growth. But the question is, how do you calculate retained earnings?
Let us find out.
1. Discover your beginning retained earnings
Start with the beginning of retained earnings, the money you kept aside at the start of the period. It’s much like finding a starting balance before you engage yourself in doing the math.
You will get beginning retained earnings on the balance sheet of the previous quarter or year. So, open the sheet, see the equity section, and know what were the beginning retained earnings at that time.
2. Check out your net income
Now, look for net income, basically a profit you earned from selling products or delivering services. Calculate the net income by taking off total expenses from the total revenue generated in the specific accounting period.
It’s the data that you will already have in your income statement or profit and loss statement. So, refer to your financial statements before adding it to the retained earnings account.
For example, if you earned $50,000 in product sales but spent only $35,000 covering other expenditures like rent, salaries, and office supplies, your net income would be $15,000.
3. Find & subtract dividends if paid
Lastly, account for any cash dividends you paid to shareholders. Figure out what share of profit you gave back to shareholders or business owners. Once found, subtract it because they are the outgoing cash, which you will neither keep with you nor reinvest for business expansion.
Therefore, separate the dividend payments from the retained earnings balance.
In case there are no dividend payouts, then skip this part and populate $0 in the retained earnings formula.
By now, you should have a clear idea of how to calculate retained earnings, but you might be wondering what’s the retained earnings formula. Here it is.
What Is the Retained Earnings Formula?
This part should be a walk in the park for you. Once you have gathered all the above-mentioned details, use the formula to calculate retained earnings.
Still Sweating Over Manual Calculations?
Let Moon Invoice do all the hard work while you drive your business forward. Generate an accurate financial statement in minutes.
How to Find Retained Earnings on Balance Sheet
Taking a closer look at the balance sheet, you will find a line item, retained or accumulated earnings, under the equity section. In case you still didn’t know how to find retained earnings on a balance sheet, follow the steps below.
- Open the company’s Balance sheet for the desired period. For example, the previous fiscal year.
- Scroll down a bit and go to the shareholders’ equity section. It would be below Assets and Liabilities.
- Here, you will find a separate line item displaying retained or accumulated earnings. Sometimes it may be labeled as Accumulated Deficit.
- Now, the balance on that line is your beginning period retained earnings.
What Is an Example of Retained Earnings?
Let’s say you launched a new business last year with retained earnings of $75,000. Your net income for the year recorded is $40,000, of which $15,000 you paid out in dividends to shareholders or business owners.
Now, after paying dividends, $25,000 from your net income is left for reinvestment. But you still use the full net income, i.e., $40,000, for the formula.
Add the leftover amount to the beginning retained earnings, and you will get the retained earnings to date. Here’s how it works:
Retained earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income (or Loss) – Dividends Paid
$100,000 = $75,000 + $40,000 – $15,000
Therefore, you can describe the ending retained earnings balance as $100,000 in the balance sheet. Plus, specify how profits were partially paid to shareholders, and the leftover balance was used to accelerate business growth.
Can Moon Invoice Help You Calculate Retained Earnings?
It does help you, but only with accurate financial data, so you don’t take more time in retained earnings calculation.
Basically, Moon Invoice or any other invoicing tool plays an indirect role, i.e., to offer you sales data, business expenses, or financial statements. You can generate high-quality and paperless reports in a few clicks and pull out the accurate data to simplify your calculations.
Moon Invoice can do the quick math when it comes to tracking revenue, refunds, or expenses. It can show you a clean picture of business financial health and provide all necessary data to measure profitability.
Here’s why it is the best bet for invoicing & accounting practices:
- Customizable invoice templates
- 20+ Online payments
- AI-powered receipt scanner
- 15+ High-quality business reports
- Smart expense management
- Bank reconciliation
- Team management
Is Manual Reporting Stealing Time and Killing Productivity?
Automate financial reporting with Moon Invoice to avoid daily headaches and reclaim your business productivity.
Final Thoughts
Retained earnings, in a nutshell, are the profits your company bagged over a specific period, minus operational costs and dividend payouts. These are the hard-earned money you can reinvest in your business to buy equipment or for advertising purposes.
By using the aforementioned retained earnings formula, you must have learned how to find retained earnings on the balance sheet and how to calculate retained earnings.
However, if you want to simplify your accounting calculations, you can get software like Moon Invoice to store and manage your important data. It will help you generate financial reports, including tax reports, in the blink of an eye and provide accurate information. Avail your free trial now.



















