Musicians and artisans have struggled to sell their art at a fair price for as long as anyone can remember!
But, for the first time, the avenues for making money as a musician have expanded beyond traditional record deals.
From streaming royalties to live shows and merchandise sales, musicians now have various opportunities to monetize their craft. With the rise in digital music and online platforms, you can choose a stable music career.
Thus, if you’re curious about how to make money with music, this comprehensive blog is for you.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Musicians must diversify their income streams and combine all income sources, such as merch, LIVE shows, and streaming services.
- Leveraging digital platforms like YouTube and Spotify helps musicians reach global audiences and enhance monetization.
- Building a strong brand increases fan loyalty and visibility, which also impacts the income.
- The biggest source of income for musicians is LIVE performance and touring.
💡Do You Know?
The global recorded-music market could grow to about $110.8 billion by 2032 under one scenario, according to a MIDiA Research report.
How to Make Money with Music?
Of course, any artist will use their talent for passive income, and the same applies to singers. But how do singers make money? You must have asked this question several times if you are an aspiring musician. The question is more common for the aspiring talents who recently entered this industry.
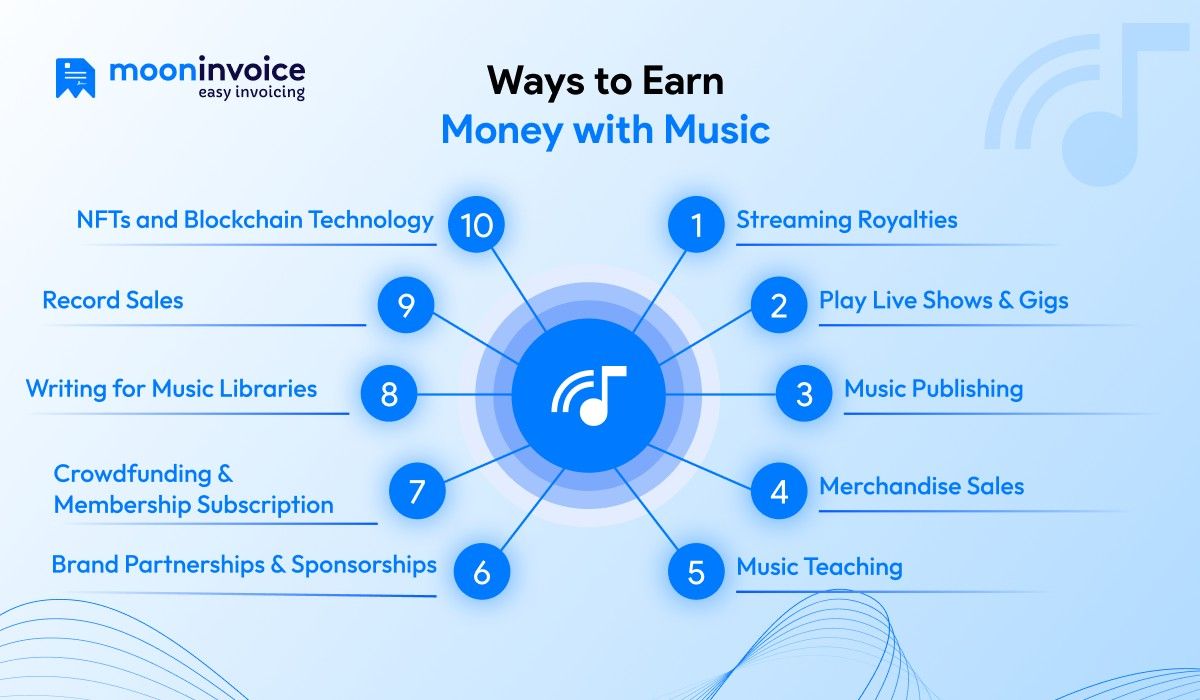
Here are 10 top approaches for artists wondering how to make money with music:
1. Streaming Royalties
Artists can earn royalties based on how often their music is streamed on services like Spotify, Apple Music, and Amazon Music.
These platforms pay artists a portion of their income per stream, which can accumulate significant revenue over time, especially for popular artists with large fan bases. To maximize streaming royalties, artists should promote their music on these platforms, encourage fans to stream their songs, and consistently release new music to keep listeners engaged. Streaming royalties are an excellent way to think about how to make money streaming music.
2. Play Live Shows & Gigs
Even in this digital era, live performances remain a staple source of income for musicians.
Fans who want genuine interactions often choose to see their favorite performers live.
From local venues to large festivals, performing live shows and gigs provides direct income from ticket sales and offers opportunities to sell merchandise like t-shirts, CDs, and posters. Additionally, live performances allow artists to connect with their fans personally, build a loyal fan base, and attract potential new listeners.
To succeed in the live music scene, artists should focus on booking gigs at suitable venues, promoting their shows effectively, and delivering memorable performances that leave a lasting impression on their audience.
3. Music Publishing
When you think about how to make money as a singer, music publishing is another way to make money. It involves licensing your music for use in various media, such as films, TV shows, commercials, and video games.
Music publishers work to place songs in these different media and collect royalties on behalf of the songwriter and composer. Artists can earn significant income through music publishing, especially if their songs are featured in popular media or become part of a successful soundtrack. To capitalize on music publishing opportunities, musicians should consider collaborating with a respected music publisher to promote their work and secure lucrative licensing deals.
4. Merchandise Sales
Once you build a loyal fan base, you can use this popularity to make money.
Selling merchandise such as t-shirts, hoodies, posters, and other branded items can be a profitable revenue stream for musicians. Music fans love supporting their favorite artists by purchasing merchandise at LIVE shows, online stores, or through retailer partnerships.
To succeed in merchandise sales, artists should invest in high-quality products that resonate with their fan base and design eye-catching items that reflect their brand identity. There are other ways to market your products, such as through live performances, email newsletters, and social media.
5. Music Teaching
Offering aspiring musicians music tuition or seminars is another strategy you must include when thinking about how musicians make money. It is a common way for artists to boost their income.
Whether teaching instrument lessons, songwriting classes, or music production workshops, music teaching can be a rewarding way to share knowledge and skills while earning money.
Artists can offer private or online music lessons, teach group classes at local music schools or community centers, or even create online courses and tutorials to reach a wider audience. To succeed in music teaching, artists should showcase their expertise, build a reputation as knowledgeable and reliable instructors, and market their teaching services effectively to attract students.
6. Brand Partnerships & Sponsorships
Collaborating with brands for endorsements, sponsorships, or product placements can provide additional income streams for musicians. Especially, it applies to those with a strong online presence.
Brands are always looking for ways to connect with their target audience through music. Partnering with musicians can help them reach new customers and enhance their brand image.
Artists can collaborate with brands in various ways. It includes endorsing products, featuring brands in music videos or social media posts, or performing at brand-sponsored events.
7. Crowdfunding & Membership Subscription Services
Platforms like Patreon, Kickstarter, and Indiegogo allow musicians to monetize their fan base by offering exclusive content and experiences in exchange for monthly subscriptions or one-time donations. Utilizing this approach is one of the best ways when it comes to how musicians make money without CDs.
Crowdfunding campaigns can help artists fund new projects, produce albums, create music videos, or finance tours. At the same time, membership subscription services provide a steady income stream in exchange for premium content and perks.
To succeed in crowdfunding and membership subscription services, artists should engage with their fans, offer compelling rewards and incentives, and communicate the value of supporting their creative endeavors. This is another important approach to consider when thinking about how singers make money.
8. Writing for Music Libraries
Writing and licensing music for music libraries can generate passive income as your music is used in projects such as films, TV shows, commercials, and video games.
Music libraries, also known as production or stock music libraries, provide a catalog of pre-made music tracks that filmmakers, advertisers, and content creators can license for their projects. Artists can submit their music to music libraries and earn royalties whenever their songs are licensed.
To succeed in writing for music libraries, artists should focus on creating high-quality, versatile, licensable music in demand for various media projects.
9. Record Sales
Many people think record sales are outdated, but they’re not! This traditional way of making money in music is still alive. No doubt, people can easily get their favorite music on platforms like Amazon Music and iTunes. But they also love buying physical records.
Musicians can easily make money by selling these records on their websites and at LIVE shows. Earnings in such cases are primarily through a royalty percentage of sales. The distribution deals, contracts, and the way music is sold determine income.
10. NFTs and Blockchain Technology
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token, referring to the sale of unique digital assets. In such a scenario, musicians mint a limited number of NFTs tied to their album or songs. Fans buy these tokens for exclusive ownership, and the NFT value increases over time. The artist continues to earn whenever the fan resells the token.
Blockchain technology plays an important role in this scenario. It is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions. Also, it ensures each NFT is unique and authentic.
Discover Seamless Invoicing Solutions for Your Music Work
Take control of your finances and streamline your invoicing process with Moon Invoice today!
Who Collects Money in the Music Industry?
Along with knowing how singers make the most money now, musicians should also be aware of the responsible entities that collect money. Here are those systems:
Performing Rights Organizations (PRO)
PRO collects money from sources such as radio stations and live music venues, then distributes it to the musicians. Joining PRO can be free or cost money. Here are some major PROs popular in the USA:
- ASCAP – Useful for composers, writers, and publishers.
- SESAC – It is an invitation-only PRO.
- SoundExchange – It is free to join for musicians and is an organization designated by the US Congress.
- BMI – It is a PRO for composers, publishers, and writers to join for free.
Mechanical Rights Organizations
When songs are reproduced or distributed, royalties are paid to composers, publishers, and songwriters. The royalties are earned every time the song is reproduced. This can be in any form, including vinyl records, pressing CDs, or streaming the songs on popular platforms.
SoundExchange
It is a U.S. organization that collects and distributes the digital performance royalties for recorded sound. Musicians are paid when their recordings are played on digital platforms. The payment can also be made to sound recording copyright holders.
Music Publishers
They collect and manage royalties related to the original song composition. This includes earnings from the mechanical licenses and synchronization.
How To Start a Recording Studio?

Starting a recording studio can be exciting for music enthusiasts and entrepreneurs. Once your name is established among the top musicians and singers, you can expand and set up your music studio.
It requires careful planning, financial backing, and meticulous attention to detail. However, it requires careful planning, investment, and attention to detail.
If you are wondering how to start a recording studio, here are some steps for you:
1. Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Before starting your recording studio and thinking over how musicians get paid, you must determine whether this is the proper business for you. Consider your love of music, your technical talents in audio engineering, your ability to manage a business, and your desire to devote time and finances to establishing and operating a recording studio.
2. Register Recording Studio Name
Choose a name for your recording studio that reflects the soul of your company and will stick in the minds of potential customers. Check whether the chosen name is available, then register it with the relevant local government or business registration agency.
3. Apply for Recording Studio Business Licenses and Permits
Look into the specific licenses and permits required to open a recording studio in your area. These may include business licenses, zoning permissions, health and safety permits, and music licensing agreements. Consult with local authorities or a business attorney to ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
4. Open a Business Bank Account
Create a corporate bank account for your recording studio to keep your personal and business finances separate. This will streamline financial management, tax reporting, and budgeting processes. Select a bank with account options that suit your needs and provide business banking services.
5. Get Business Insurance
Protect your recording studio against potential risks and liabilities by obtaining adequate business insurance coverage. Consider insurance policies covering property liability, general liability, equipment liability, and professional liability. Speak with an insurance agent who specializes in small businesses to evaluate your insurance needs and choose the appropriate policy.
6. Essential Software and Tools
Investing in essential software and tools is crucial for running a recording studio efficiently. Here are some key software and tools you’ll need:
- Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): When recording, editing, mixing, or mastering audio, choose a reliable DAW. Popular DAWs include Studio One, Logic Pro, Ableton Live, FL Studio, and Pro Tools.
- Audio Interfaces and Converters: Invest in high-quality audio interfaces and analog-to-digital converters to capture and process audio signals from microphones and instruments.
- Microphones and Headphones: Acquire a diverse collection of microphones suitable for recording vocals, instruments, and other sound sources. Invest in studio-quality headphones for monitoring and playback during recording sessions.
- Studio Monitors and Acoustic Treatment: Install studio monitors (speakers) with accurate frequency response and acoustic treatment to ensure an optimal listening environment for mixing and mastering. Acoustic treatment includes sound-absorbing panels, bass traps, and diffusers that diminish room reflections and resonance.
- Invoicing Software: If you want to turn a profit for your studio, you must manage your finances well. Manage your recording studio’s finances efficiently using invoicing software like Moon Invoice to create and send professional invoices to clients, track payments, and manage billing cycles. Look for invoicing software that offers a customizable musician invoice template, automated invoicing, payment reminders, and reporting features.
Is It Hard to Get On-Time Payment as a Musician?
No more with Moon Invoice! Share a clear & impressive invoice with your client through our ready-made templates.
How Much Does it Cost to Start a Recording Studio Business?
The cost of starting a recording studio business varies significantly depending on location, size, equipment quality, and business model.
Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the probable costs connected with opening a recording studio.
1. Studio Space
The cost of studio space can vary based on location, size, and amenities. Renting a commercial space in a prime location with suitable acoustic characteristics can be expensive. Converting an existing space into a studio may require renovation and soundproofing, adding to the overall cost.
2. Equipment
Investing in high-quality recording equipment is essential for delivering professional audio recording and production services. Equipment costs can vary by brand, specifications, and quantity. Here are some essential equipment estimated costs:
- Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): $200 – $600+
- Audio Interface: $100 – $1000+
- Microphones: $100 – $3000+
- Studio Monitors: $200 – $3000+
- Headphones: $50 – $500+
- Cables, Stands, and Accessories: $200 – $500+
- Acoustic Treatment: $500 – $2000+
3. Furniture and Fixtures
Furnishing the studio with desks, chairs, storage cabinets, and acoustic furniture increases startup costs. Additionally, installing lighting fixtures, wiring, and electrical outlets may require professional assistance.
4. Software and Plugins
Aside from the DAW, investing in additional software and plugins for recording, mixing, and mastering is necessary. Software and plugins can range in price from free to hundreds or even thousands of dollars per license.
5. Business Licenses and Permits
Obtaining essential business licenses and permits from local authorities costs money, and the costs may vary depending on the area and requirements.
6. Marketing and Promotion
Allocating a budget for marketing and promotion is essential to attract clients and establish a presence in the industry. Costs may include website development charges, branding materials, advertising, and promotional campaigns.
7. Insurance
Purchasing business insurance to protect against liabilities, equipment damage, and other risks is crucial. The location, size, and coverage all affect how much insurance costs.
8. Miscellaneous Expenses
Additional expenses may include utilities, internet service, professional fees (legal, accounting), and ongoing maintenance and upgrades.
Total Startup Cost Estimate
Considering the various expenses outlined above, the total startup cost to launch a recording studio business can range from approximately $160,000 to $550,000, depending on equipment quality, studio size, and location-specific costs.
How Much Should You Charge for Recording Studio Time?
Determining how much to charge for recording studio time depends on several factors. After figuring out how music makes money or how living room concert sessions work, you need to make a plan.
Here’s a breakdown of considerations to help you determine an appropriate rate:
1. Studio Expenses
Calculate your studio’s operating expenses, including rent, utilities, equipment maintenance, insurance, software licenses, and other overhead costs. Divide these expenses by the monthly hours you expect to operate the studio to determine your baseline cost per hour.
2. Equipment Quality and Amenities
Consider the quality of your studio’s recording equipment, acoustics, and amenities. Studios with high-end equipment, acoustically treated rooms, and additional amenities like a lounge area or refreshments may justify higher rates.
3. Market Demand and Competition
Research the rates charged by other recording studios in your area and assess the demand for recording services. You can set higher rates when demand is high and competition is limited.
4. Experience and Expertise
Consider your experience, knowledge, and status in the sector. Studio heads with a track record of successful projects may expect higher fees due to their perceived value and experience.
5. Client Budgets and Project Scope
Consider your target clients’ budgets and the scope of their projects. Clients may have varying budgets and expectations for their recording projects, so be prepared to offer flexible pricing options based on the required services.
6. Specialized Services and Packages
Offering specialized services such as mixing, mastering, vocal coaching, or instrument rental may allow you to charge higher rates for additional services. Consider creating packages or bundled services to provide value to clients while maximizing your earnings.
7. Pricing Structure
Determine your pricing structure based on characteristics such as hourly, half-day, or full-day rates, or project-based pricing. Hourly rates are common for short recording sessions, while half-day or full-day rates may be more suitable for longer sessions or multiple projects.
8. Value-added Services
Consider offering value-added services such as free initial consultations, flexible booking options, discounts for repeat clients, or promotional offers to attract and retain clients.
Rock Your Music & Billing with Ease!
Level up your invoicing game and enhance your music business performance using our ready-to-use musician invoice template.
Final Words
Here we are wrapping things up on how singers make money. When you decide to sell music online as a musician, it requires skill, dedication, and an entrepreneurial mindset.
By diversifying income streams and exploring opportunities beyond traditional music sales, musicians today can build sustainable careers in the music industry. Additionally, starting a recording studio business can provide a platform for aspiring artists while creating a fulfilling entrepreneurial venture.
After your firm is properly established, you will need to manage your funds. Tools like Moon Invoice will help you with this while you can concentrate on your artistic endeavors. Here is Free Sign Up!



















